
How to Calculate an International Cost-of-Living Index
2025-04-07
Global mobility is on the rise, and understanding the Cost-of-Living in different locations is essential for professionals relocating abroad. A Cost-of-Living Index (COLI) helps quantify these differences, assisting employers and employees alike in planning compensation packages. This article provides a clear guide on how to calculate a COLI and apply it in salary decisions, focusing on the needs of global mobility professionals and expats.
Definition of Cost-of-Living
Cost-of-Living refers to the amount of money required to maintain a particular standard of living in a specific location. It includes everyday expenses like housing, groceries, transportation, and healthcare. When people move from one city to another, their total spending will likely change because some items may cost more or less in the new location.
Definition of a Cost-of-Living Index
A Cost-of-Living Index (COLI) is a measure that compares the Cost-of-Living between different locations or over time. Typically, a base location is assigned an index value of 100, and other locations are compared against it. For instance, if City A has an index of 140, it means City A is 40% more expensive than the base location.
What Can a Cost-of-Living Index Be Used For?
COLI data is used in various ways:
- Salary adjustments: It ensures an expat or professional moving abroad receives a fair salary that maintains their standard of living.
- Global mobility compensation planning: Companies use COLI to design relocation packages.
- Cost-of-Living allowances: It helps calculate expat Cost-of-Living allowances, so professionals are adequately compensated for higher living costs abroad.
What Data is Needed to Calculate a Cost-of-Living Index?
To create a COLI, you need prices of the same goods and services in multiple locations. These goods and services are grouped into categories, often called baskets. For instance, Xpatulator, uses the prices for over 200 goods and services grouped into 13 basket groups such as groceries, housing, and healthcare. The price data is sourced globally from a wide range of reliable suppliers and regularly updated.
How Quickly Can a Cost-of-Living Index Go Out of Date?
Prices fluctuate, driven by factors like inflation, currency changes, and local economic conditions. This means a COLI can quickly become outdated if not regularly updated. Xpatulator, like other leading providers, update the COLI data quarterly to ensure accuracy.
Why Does the Cost-of-Living Go Up and Down in One Location Relative to Another?
Several factors cause Cost-of-Living differences between locations:
- Inflation: Rising prices in one location increase its COLI compared to others.
- Currency fluctuations: A weaker currency makes a location cheaper for expats paid in a stronger currency.
- Supply and demand: Housing shortages, for instance, can drive up rent, significantly impacting COLI.
Why is the Cost-of-Living for an Expat Different from a Local Employee?
Expats often face different costs than locals. For example, they may pay higher rents due to living in expat-friendly neighborhoods. They may choose to buy food and beverage brands from their home country which are costly to import and are often priced substantially higher than a local equivalent. They may also face additional costs, such as international schooling or private healthcare, which are less relevant for local employees.
The Maths: Formula Methodology and Steps for Calculating a Cost-of-Living Index
Calculating a COLI involves gathering prices of the same items in two locations. These prices are then weighted by their importance in an expat’s budget. For instance, housing may be given more weight than groceries because expats spend a higher portion of their salary on rent.
Here’s a simple formula:
- COLI = (Cost in Location A / Cost in Location B) * 100
- For example, if the cost of the basket in Location A is 129, and in Location B it is 92, the COLI is:
- COLI = (129 / 92) * 100 = 140.2
- This means Location A is 40.2% more expensive than Location B.
Practical Examples Using the Methodology
Consider a company headquartered in City X (COLI 100), sending employees to City Y (COLI 150). The company wants to ensure its employees maintain the same standard of living in the new city. If an employee earns $100,000 in City X, the formula would be:
- $100,000 * (150/100) = $150,000
- This means the employee would need a $50,000 increase to maintain their lifestyle in City Y.
Applying a Cost-of-Living Index to a Salary Calculation
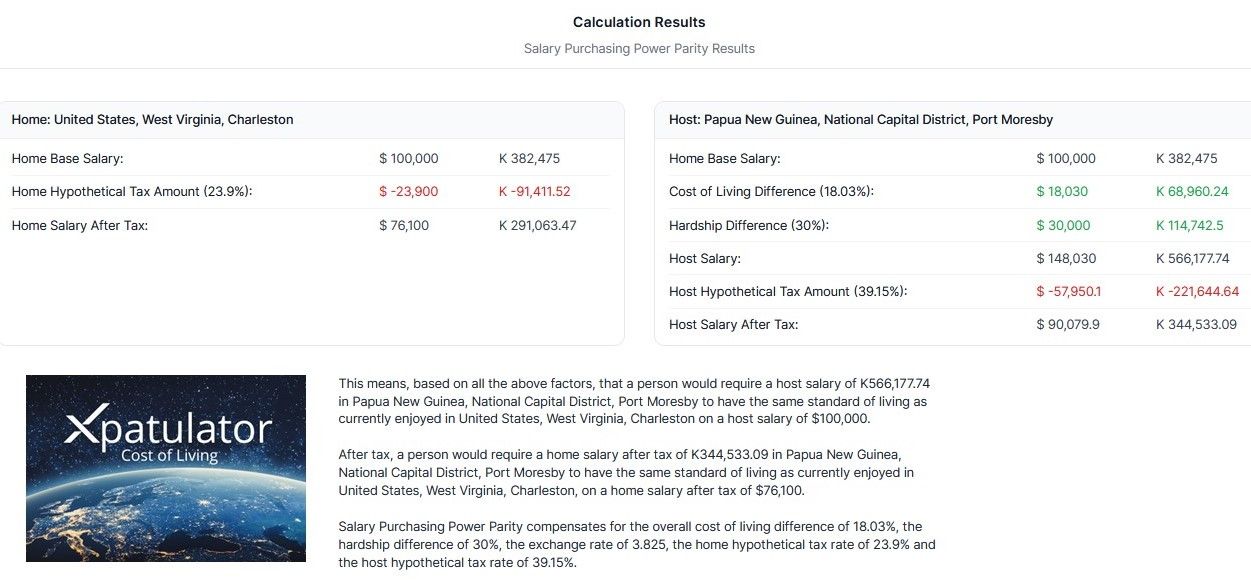
When planning an international assignment, a COLI helps ensure employees can maintain their lifestyle. Using a Global Mobility Salary Calculator like Xpatulator’s Salary Purchasing Power Parity Calculator (SPPP), you can adjust for differences in Cost-of-Living, exchange rates, and hardship.
Take an example where an employee earning $100,000 in the U.S. moves to Switzerland, with a COLI of 140. If the employee faces a 10% hardship premium, their new salary would be:
- $100,000 * 1.40 * 1.10 = $154,000
- This ensures their salary matches the higher Cost-of-Living and hardship in Switzerland.
How Does Xpatulator Collect Data and Prepare Cost-of-Living Indexes?
Xpatulator gathers data on 13 baskets of goods and services from over 780 global locations. They update their data quarterly, ensuring the most accurate comparisons. The basket groups include items like:
- Housing: The largest expense for most expats.
- Groceries: Weighted based on expatriate spending patterns.
- Healthcare: Important for locations where expats need private services.
How Cost-of-Living Indexes Are Used in Xpatulator Calculators
Xpatulator’s tools, like their free Basic Salary Purchasing Power Parity Calculator and the premium Salary Purchasing Power Parity Calculator, Cost of Living Allowance Calculator, Cost of Living Indexes Calculator and the International Assignment Management Calculator, apply COLI to calculate appropriate compensation for expats. By inputting base salary and COLI values, the calculators determine the correct adjustment needed to maintain purchasing power abroad.
Conclusion A Cost-of-Living Index provides a vital tool for expats and global mobility professionals. It ensures consistent standards of living when employees move between locations, offering a clear way to adjust salaries. By understanding COLI calculations and using tools like Xpatulator, companies can ensure fair compensation and better manage international assignments.
Use Xpatulator’s Cost-of-Living Calculators and Tools for informed decision-making about the Cost-of-Living in 780 global locations, and the salary / allowance / assignment package required to maintain your international assignee’s current standard of living.